Not just grammar
短语
Widnow traveling 冲浪式穷游
make 面罩/口罩
have a picnic 野餐
take part in 参加
go fishing 钓鱼
free 空闲
hurry up 赶快
PE teacher 体育老师
use up 用光 用完
study hard 努力学习
snacks 零食
Hand up 举起手来
a good score 一个很好的成绩
work hard 努力工作
earn much money 挣很多钱
immediately 立刻,马上
air conditioning 空调
score、mark 分
learning strategies 学习方式/学习侧率
public relation dept 公关部门
trade 贸易
marketing depot 营销仓库
finance dept 财务部
Purchasing(Procurement) dept 采购(采购)部门
purchase、buy 购买
after - sale service dept 售后服务部
traffic warden 交通督导员
tour guide 导游
tailor 裁缝、裁缝师
cloth clothes clothing 布
blacksmith 铁匠
doorman 看门人
bellboy 服务生
anchor 锚
shoemaker 鞋匠
gas station attendant 加油站服务员
flight attendant 空姐
nun 尼姑
clown 小丑
airline representative 航空代表
salesmen or salesman 推销员或推销员
passion 情
persuasive persuade 有说服力的
enterprising enterpring 进取
ambition 志向
enthusiastic 热情
shrewd(smart) 精明(聪明)
boastful 自夸自擂
tricky 狡猾
Teachers 教师
knowledgeable 懂行
patient,tolerant 患者,宽容
humorous 幽默
warm-hearted 热心
enthusiastic 热情
considerate 周到、细心
Doctors 医生
skillful 熟练
brave,calm 勇敢、冷静
confident cure 自信治愈
careful 小心
sympathetic 有同情心
Policemen 警察
brave 勇敢
quick quick
watchful 注意的
responsible 主管
percipient 知觉的
Accountants 会计师
cautious 谨慎
honest 诚实
accurate 准确
thoughtful aspects 体贴的方面
人称
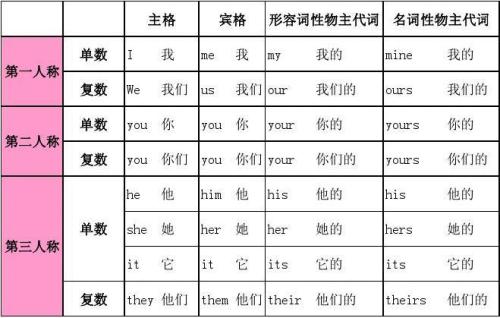
第一人称: 我、我们
第二人称: 你、你们
第三人称 他、她、它、他们、她们、它们
主格和宾格的区别在于:
在句子中,主格(the nominative case)用作主语,宾格(the objective case)用作宾语。
一般来说,人称代词里的主格放在句首做主语和表语,宾格放在句末或句中做动词和介词的宾语。打个比方,主人邀请宾语,主格就像主人,宾格就像宾客。主格在动词前面,宾格在动词或介词后面。
根据人称代词在句中所充当的成分可以分为主格人称代词、宾格人称代词。人称代词有单复数之分。
例句:
主格:
- I am a beautilful gir.
我是一个漂亮的女孩 - You are a clever boy.
你是一个聪明的男孩 - He is a driver.
他是一名司机 - She is a very nice nurse.
她是一位非常好的护士 - We are chinese.
我们是中国人 - You are all in order.
你们都井井有条 - They are all good students.
他们都是好学生
宾语:
- Excuse me,can you tell me how to get the mall?
打扰一下,请问你能告诉我怎么去商场吗? - Can I help you?
我能帮助你吗 - Please take good care of her.
请好好照顾她 - The old man gave us a big smile.
这位老人给了我们一个灿烂的笑容 - The teacher will ask you to finish your homework on time.
老师会要求你准时完成作业 - Who can help them?
谁可以帮助他们?
语法
正确形式: I like reading books
错误形式: I like read book read 后面加动词,不应该加名词
引导的条件状语从句
was 是is的过去式,用于第三人称单数
were 是are的过去式,用于第二人称及第三人称复数形式
由引导词if或unless引导的状语从句叫做条件状语从句。在英文中,条件是指某一件事情实现之后(状语从句中的动作),其它事情(主句中的动作)才能发生,通常译作假如。
注意: 在含有条件状语从句的符合句中,表示将来时态,主句是一般将来时态,祈使句或情态动词,从句要用现在时态,主将从现原则(主将从现,将并非指将来时,还指表示将来含义的,跟着if后的那句话是从句。)
if
表示在某种条件下某事很可能发生。
- If you ask him,he will help you.
如果你请他帮忙,他会帮你的。 - If you fail in the exam,you will let him down.
如果你考试不及格,你会让他失望的 - If引导的条件状语从句即可以将从句放前面也可以将从句放后面
- If it rains,we will stop playing.
如果天下雨,我们就不玩了 - We will stop playing,if it rains.
如果天下雨,我们就不玩了
- If it rains,we will stop playing.
- We will have a picnic if it’s sunny tomorrow.
如果明天是请她,我们去野餐 - Dad will buy a pen for me if I take part in the enblish compeition
如果我参加英语比赛,爸爸将帮我买钢笔。 - We will go to the part if it doesn’t rain tomorrow.
如果明天不会下雨我们就去参加
主情从现有can、may、must、should、you feel hungry等情态动词
指如果句子中有情态动词那么情态动词后加一般现在时的动词即动词原型
If you feel hungry,you should eat something. 如果你感到饥饿,你应该吃点东西
主将从现 If you ..... you will....
- 错误形式: If you won’t hurry up,you will miss the early bus.
如果你不快点,你会错过早班车。 - 正确形式: If you don’t hurry up,you will miss the early bus.
如果你不快点,你会错过早班车。 - You must stop if the traffic light is red.
交通灯红色的时候你必须停下 - You may go fishing if you are free.
如果你有空,你可以去钓鱼 - He can go home if he finishes his homework.
如果他完成作业,就可以回家了。
主祈从现动态词开始
祈使句一般开头是以do、let、don’t、never、to do开头
- Let me know if he comes.
如果他来,请告诉我 - Don’t wait for me if I am late.
如果我来迟了,不用等我。 - Put up your hands if you have any questions.
如果您有任何疑问,请举手 - If I study hard,I’ll win the english competition.
如果我努力学习,我将赢得英语比赛。
总结:主要看句中有没有if、when、as soon as……这些词有时代表主将从现、主祈从现、主情从现。注意:when有时可以和延续性动词连用,也可以和短暂性动词连用。
例如: when I was get there,he was singing in the KTV. 当我到达那里时,他正在KTV唱歌。
unless = if…not.
If在条件状语从句中标识如果,在位于动词之后引导宾语从句表示是否,相当于whether(是否).
- If you don’t leave now, you will be late for school.
如果你不现在走,你就会上学迟到 - If you leave now,you don’t be late for school.
如果你现在走,你上学不会迟到。 - Unless you leave now,you will be late for school.
除非你现在走,否则你就上学迟到。 - If you don’t clean your teeth,you will have a toothache.
如果你不清洁牙齿,你会牙疼。 - Unless you clean your teeth,you will have a toothache.
除非你清洁你的牙齿,否则你会牙疼。 - If you don’t put the air conitioning on soon,this room will get very hot.
如果你不尽快打开空调,这个房间会很热。 - Unless you put the air conditioning on soon,this room will get very hot.
除非你很快就打开空调,否则这个房间会很热。 - Do you know if he will come back next week?
你知道他下周会不会回来 - If I knew the questions of the exam,I would get the highest mark this time.
如果我知道考试的问题,这次我会得到最高分。 - If I were you,I never do this!
我要是你,我绝非如此!当然在特定的虚拟语气时态下,就要使用were,不要使用was。这里就是要使用复数形式,不能用was,这在虚拟语气中是规定
真是条件句和非真实条件句两种
fact 事实
wish 愿望 -> 不切实际与事实相反
If条件句:真是条件句和非真实条件句两种
a真实条件句:条件是真的或有可能实现的,采用陈述语气
b非真实条件句:条件是无法实现或几乎无法实现的,采用虚拟语气
虚拟语气:主语 + 过去式
If 非真实条件句
与现状事实相反
从句if + 主语 + were/动词过去时
主语主语 + would/should/might/could + 动原
- If you were the last man is the world,I would definitely remain single.
如果你是世界上最后一个人,我肯定会保持单身。 - If Li Gang were your father,I would marry you.
如果李刚是你的父亲,我会嫁给你 - If the sun rose in the west, I would marry you.
如果西方的太阳升起,我会嫁给你。
If 非真实条件句
与过去事实相反
从句If + 主句 + had done
主句主语 + would have done
- If he had driven more carefully,he would not have had the car accident yesterday.
如果他小心驾驶,他昨天就不会发生车祸。 - If I had learned how to swim,I would not have been trapped in this island.
如果我学会了如何游泳,我就不会被困在这个岛上。 - If I had learned english hared , i would have gone abroad.
如果我学会了英语,我就会出国了 - If we had not broken up
如果我们没有分手